Virtualization and Hypervisors for Small Business
In recent years, virtualization has become an increasingly popular technology for businesses of all sizes. Essentially, virtualization allows you to create multiple virtual machines (VMs) that can run different operating systems and applications on a single physical server. This can be incredibly beneficial for small businesses, as it allows them to make better use of their resources, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
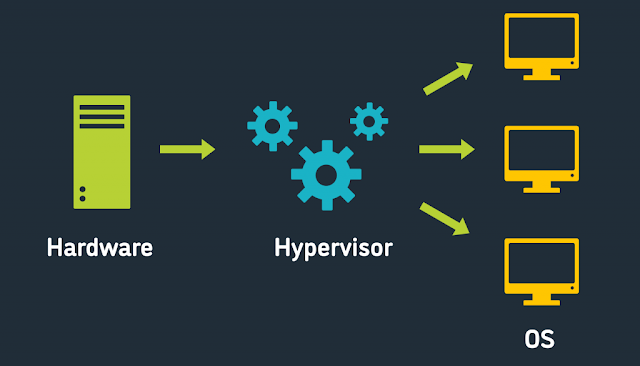
At the heart of virtualization is the hypervisor, which is the software that manages the VMs and allows them to
run on a single physical server. There are two main types of hypervisors: Type
1 and Type 2.
Type 1 hypervisors, also known as
bare-metal hypervisors, run directly on the host's hardware, allowing them to
provide excellent performance and stability. They are typically used in
enterprise-level data centers, but they can also be used by small businesses
that require high performance and reliability.
Type 2 hypervisors, on the other
hand, run on top of an existing operating system, and are often used for
desktop virtualization or testing and development environments. While they can
be easier to set up and use, they may not provide the same level of performance
and stability as Type 1 hypervisors.
So, why might a small business want
to use virtualization and hypervisors? Here are a few key benefits:
- Better
resource utilization: By running
multiple VMs on a single physical server, you can make better use of your
hardware resources, reducing the need for additional servers and
potentially saving money on hardware costs.
- Improved
scalability: As your business grows,
you can easily add new VMs to your existing infrastructure, without having
to worry about purchasing additional hardware.
- Reduced
downtime: If one VM goes down, the
others can continue to run without interruption, reducing the risk of
downtime and data loss.
- Improved
security: By isolating different
applications and operating systems on separate VMs, you can reduce the
risk of security breaches and protect your data.
- Easier
management: With virtualization, you
can manage multiple servers and applications from a single console, making
it easier to monitor and maintain your infrastructure.
Of course, there are also some potential
downsides to virtualization and hypervisors, such as increased complexity and
the need for additional hardware resources to run the hypervisor software.
However, for many small businesses, the benefits can outweigh these drawbacks,
making virtualization and hypervisors a smart choice for improving efficiency,
reducing costs, and improving overall IT operations.
How to Choose the Right Hypervisor for Your
Needs
Choosing the right hypervisor for
your needs can be a challenging task, as there are many different options
available on the market. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a
hypervisor:
- Performance:
The performance of the hypervisor is a critical factor to consider,
especially for businesses that require high levels of performance and
reliability. Type 1 hypervisors tend to offer better performance and
stability than Type 2 hypervisors.
- Cost:
The cost of the hypervisor is another important consideration. Some
hypervisors, such as VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V, are commercial
products that require a license fee, while others, such as KVM and Xen,
are open-source and free to use.
- Scalability:
If your business is likely to grow, it's important to choose a hypervisor
that can scale easily. Some hypervisors are better suited for small
businesses, while others are designed to handle large-scale data centers.
- Management:
The ease of management is another critical factor to consider. Look for a
hypervisor that offers a centralized management console, which makes it
easier to manage multiple virtual machines and servers from a single
location.
- Compatibility:
It's important to choose a hypervisor that is compatible with your
existing hardware and software. For example, some hypervisors may not
support certain operating systems or applications.
- Support:
Finally, it's important to choose a hypervisor that is backed by a strong
support team. Look for a hypervisor vendor that offers comprehensive
support, including training, documentation, and technical assistance.
By considering these factors, you
can make an informed decision about which hypervisor is right for your
business. Keep in mind that there is no one-size-fits-all solution, and the
best hypervisor for your business will depend on your specific needs and
requirements.
There are several popular hypervisor
technologies on the market today. Here's a brief comparison of some of the most
commonly used hypervisors:
- VMware
vSphere: VMware vSphere is a Type
1 hypervisor that is widely used in enterprise-level data centers. It is
known for its high performance, stability, and robust feature set. It
supports a wide range of operating systems and applications, and offers
advanced management tools and automation capabilities. VMware vSphere is a
commercial product that requires a license fee.
- Microsoft
Hyper-V: Microsoft Hyper-V is a
Type 1 hypervisor that is included with the Windows Server operating
system. It is designed to be easy to use and offers a range of features,
including support for live migration and high availability. Microsoft
Hyper-V is a commercial product that requires a license fee.
- KVM:
KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a Type 1 hypervisor that is part of
the Linux kernel. It is an open-source hypervisor that is free to use and
offers excellent performance and scalability. KVM supports a wide range of
operating systems and applications and is commonly used in cloud
environments.
- Xen:
Xen is a Type 1 hypervisor that is also open-source and free to use. It is
widely used in cloud environments and supports a range of operating
systems and applications. Xen offers good performance and scalability and
is known for its strong security features.
- Oracle
VirtualBox: Oracle VirtualBox is a
Type 2 hypervisor that is free to use and available on multiple platforms,
including Windows, Linux, and macOS. It is designed for desktop
virtualization and testing and development environments and offers a range
of features, including support for snapshots and virtual networking.
Each of these hypervisors has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the best option for your business will depend on your specific needs and requirements. It's important to evaluate each hypervisor carefully and consider factors such as performance, cost, scalability, management, compatibility, and support before making a decision.





Comments
Post a Comment